The cocoa bean is one of the most important agricultural export products of Indonesia. In the past 25 years, the Indonesian cocoa sector has experienced massive growth, driven by rapid expansion of smallholder farmer participation. Indonesian smallholders contribute – by far – most of the national production, thus outperforming big state plantations and large private estates. The country currently has approximately 1.5 million hectares of cocoa plantations.
Indonesia’s main locations of cocoa production are:
- Sulawesi
2.North Sumatra
3. West Java
4. Papua
5. East Kalimantan

Indonesia cocoa map
The main Indonesian cocoa producing region is the island of Sulawesi which accounts for around 75 percent of Indonesia’s total cocoa production. As Indonesia’s cocoa productivity per hectare has been lagging behind that of other cocoa-producing countries, the government started a five-year cocoa revitalization program in 2009 to boost production through intensification, rehabilitation and rejuvenation activities, covering a total area of 450 thousand hectares. Factors that are hampering progress in the cocoa industry are aging trees (planted in the 1980s), insufficient improved planting materials and little farm maintenance. More investment in this sector is needed to reach the government’s one million tonnes annual production target by 2013-2014.
In terms of export, cocoa forms Indonesia’s fourth largest foreign exchange earning from the agriculture sector (after palm oil, rubber and coconut). However, the majority of Indonesia’s cocoa export constitutes raw beans instead of processed cocoa, meaning that Indonesia loses out on added value revenues. The most important destination countries for Indonesia’s cocoa beans are Malaysia, the USA and Singapore.
The table below shows Indonesia’s national cocoa production and export.
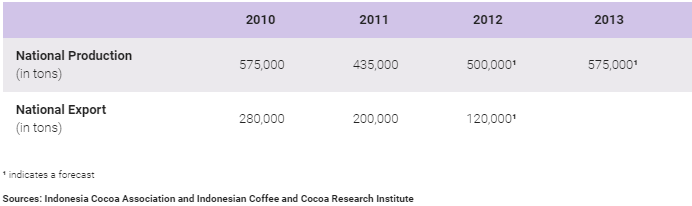
Indonesia’s national cocoa production and export
